Cybersecurity teams are working feverishly to stem the impact of the single biggest global ransomware attack on record, with some details emerging about how the Russia-linked gang behind it breached the company whose software was the conduit.
An affiliate of the notorious REvil gang, best known for extorting $11 million from the meat-processor JBS after a Memorial Day attack, infected thousands of victims in at least 17 countries on Friday, largely through firms that remotely manage IT infrastructure for multiple customers, cybersecurity researchers said.
REvil was demanding ransoms of up to $5 million, the researchers said. But late Sunday it offered in a posting on its dark web site a universal decryptor software key that would unscramble all affected machines in exchange for $70 million in cryptocurrency.
Earlier, the FBI said in a statement that while it was investigating the attack its scale “may make it so that we are unable to respond to each victim individually.” Deputy National Security Advisor Anne Neuberger later issued a statement saying President Joe Biden had “directed the full resources of the government to investigate this incident” and urged all who believed they were compromised to alert the FBI.
Mr. Biden suggested Saturday the U.S. would respond if it was determined that the Kremlin is at all involved. Less than a month ago, he pressed Russian President Vladimir Putin to stop giving safe haven to REvil and other ransomware gangs whose unrelenting extortionary attacks the U.S. deems a national security threat.
On Monday, Putin spokesman Dmitry Peskov was asked if Russia was aware of the attack or had looked into it. He said no, but suggested it could be discussed by the U.S. and Russia in consultations on cybersecurity issues for which no timeline has been specified.
Dutch researchers said they alerted Miami-based Kaseya to the breach and said the criminals used a “zero day,” the industry term for a previous unknown security hole in software. Voccola wouldn’t confirm that or offer details of the breach – except to say that it wasn’t phishing.
“The level of sophistication here was extraordinary,” he said.
When the cybersecurity firm Mandiant finishes its investigation, Voccola said he is confident it will show that the criminals didn’t just violate Kaseya code in breaking into his network but also exploited vulnerabilities in third-party software.
It wasn’t the first ransomware attack to leverage managed services providers. In 2019, criminals hobbled the networks of 22 Texas municipalities through one. That same year, 400 U.S. dental practices were crippled in a separate attack.
One of the Dutch vulnerability researchers, Victor Gevers, said his team is worried about products like Kaseya’s VSA because of the total control of vast computing resources they can offer. “More and more of the products that are used to keep networks safe and secure are showing structural weaknesses,” he wrote in a blog Sunday.
The cybersecurity firm ESET identified victims in least 17 countries, including the United Kingdom, South Africa, Canada, Argentina, Mexico, Indonesia, New Zealand and Kenya.
Kaseya says the attack only affected “on-premise” customers, organizations running their own data centers, as opposed to its cloud-based services that run software for customers. It also shut down those servers as a precaution, however.
Kaseya, which called on customers Friday to shut down their VSA servers immediately, said Sunday it hoped to have a patch in the next few days.
Active since April 2019, REvil provides ransomware-as-a-service, meaning it develops the network-paralyzing software and leases it to so-called affiliates who infect targets and earn the lion’s share of ransoms. U.S. officials say the most potent ransomware gangs are based in Russia and allied states and operate with Kremlin tolerance and sometimes collude with Russian security services.
Businesses around the world are attacked using ransomware roughly every 11 seconds, according to Cybersecurity Ventures. The security firm projects that global ransomware losses this year will reach $20 billion.
Cybersecurity expert Dmitri Alperovitch, of the Silverado Policy Accelerator think tank, said that while he doesn’t believe the Kaseya attack is Kremlin-directed, it shows that Putin “has not yet moved” on shutting down cybercriminals.
OVERVIEW
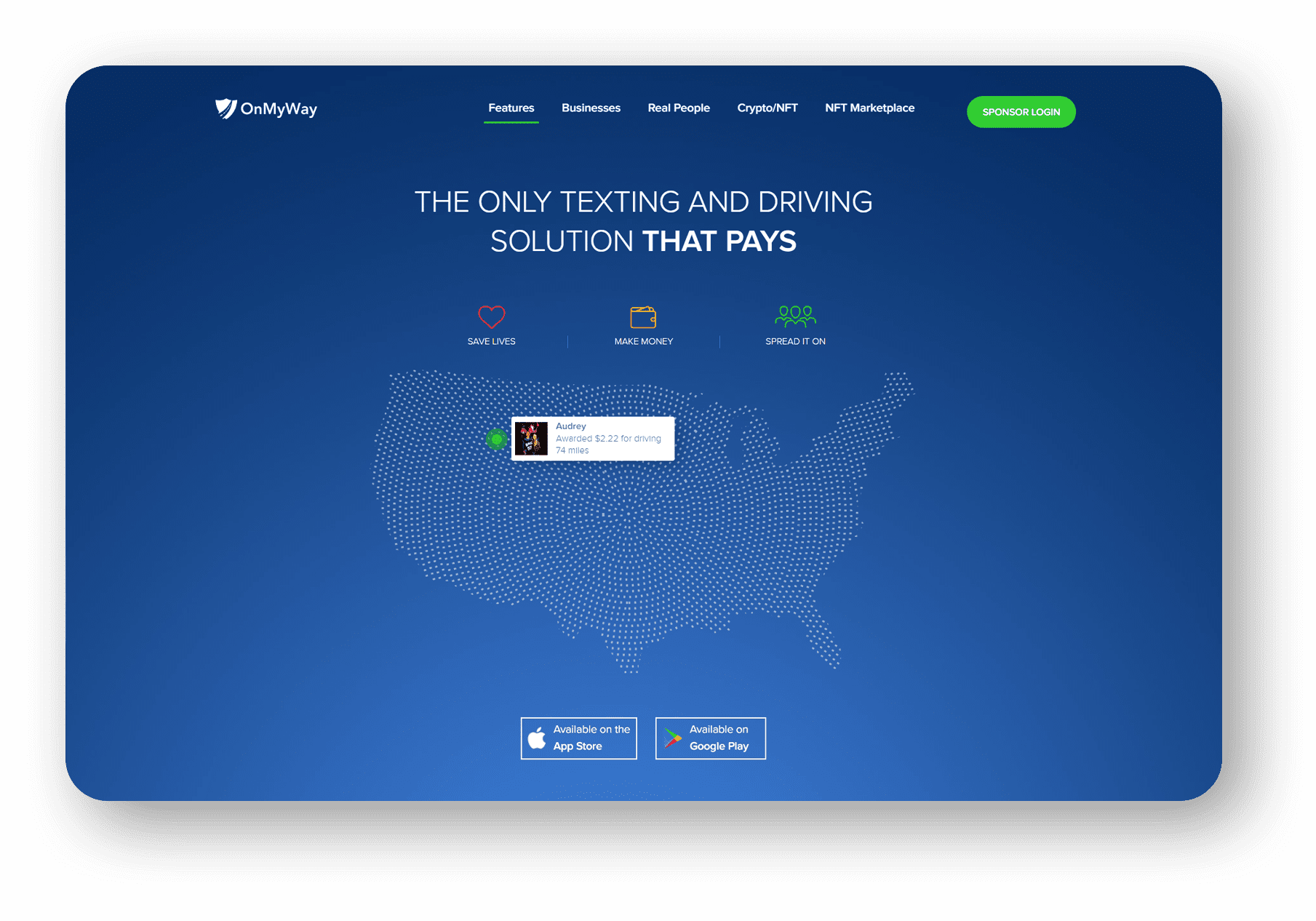
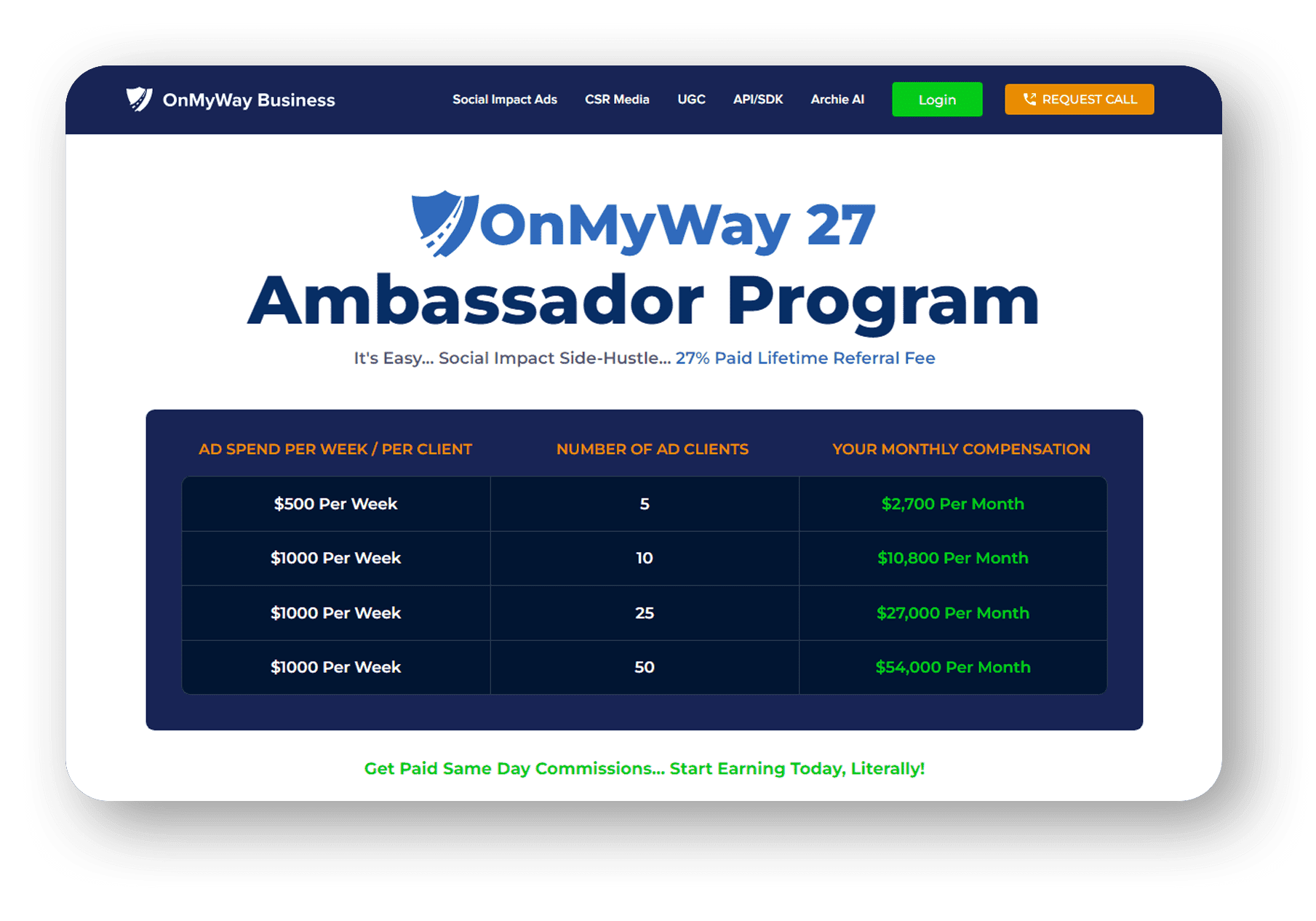
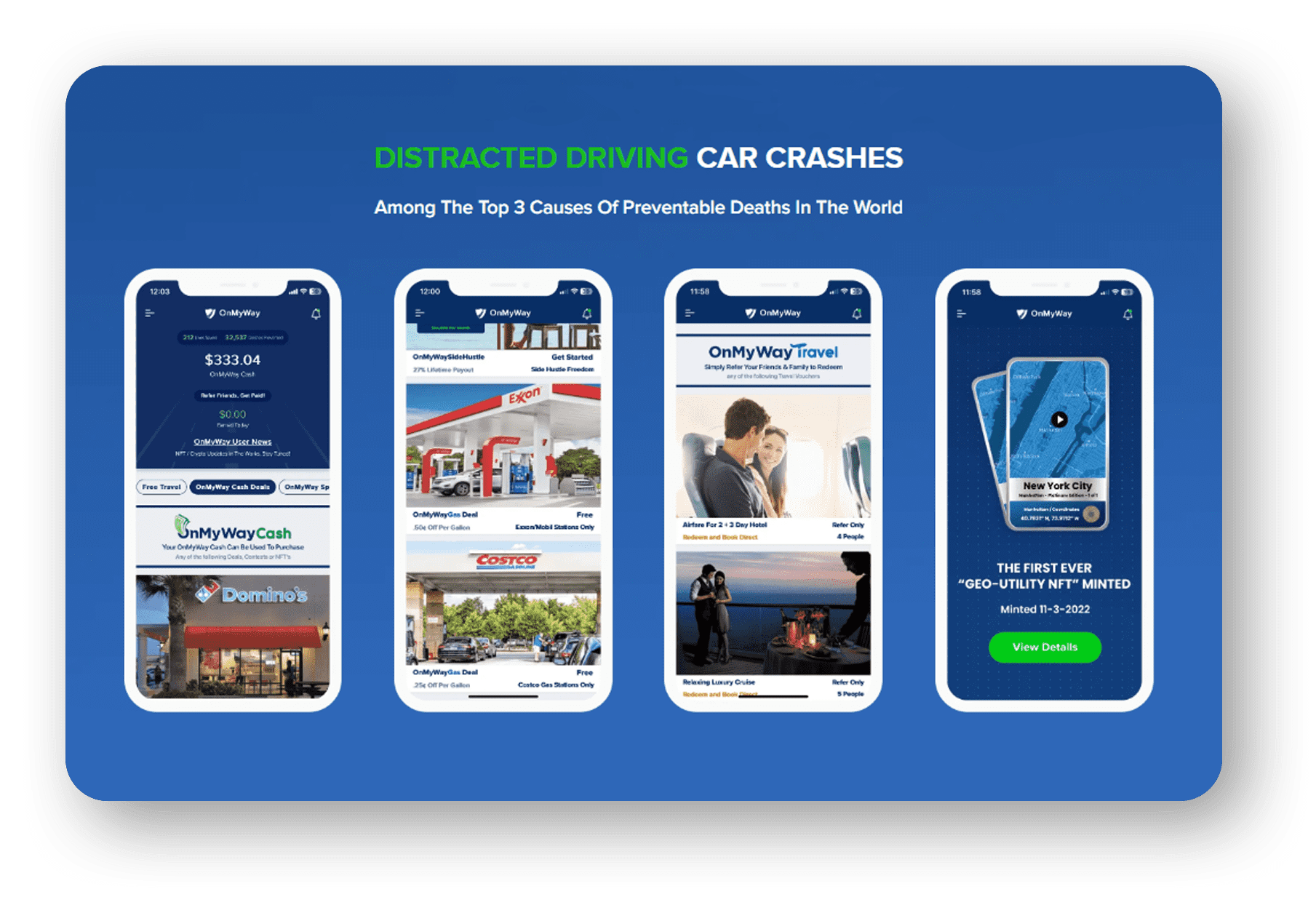
OnMyWay Is The #1 Distracted Driving Mobile App In The Nation!
OnMyWay, based in Charleston, SC, The Only Mobile App That Pays its Users Not to Text and Drive.
The #1 cause of death among young adults ages 16-27 is Car Accidents, with the majority related to Distracted Driving.
OnMyWay’s mission is to reverse this epidemic through positive rewards. Users get paid for every mile they do not text and drive and can refer their friends to get compensated for them as well.
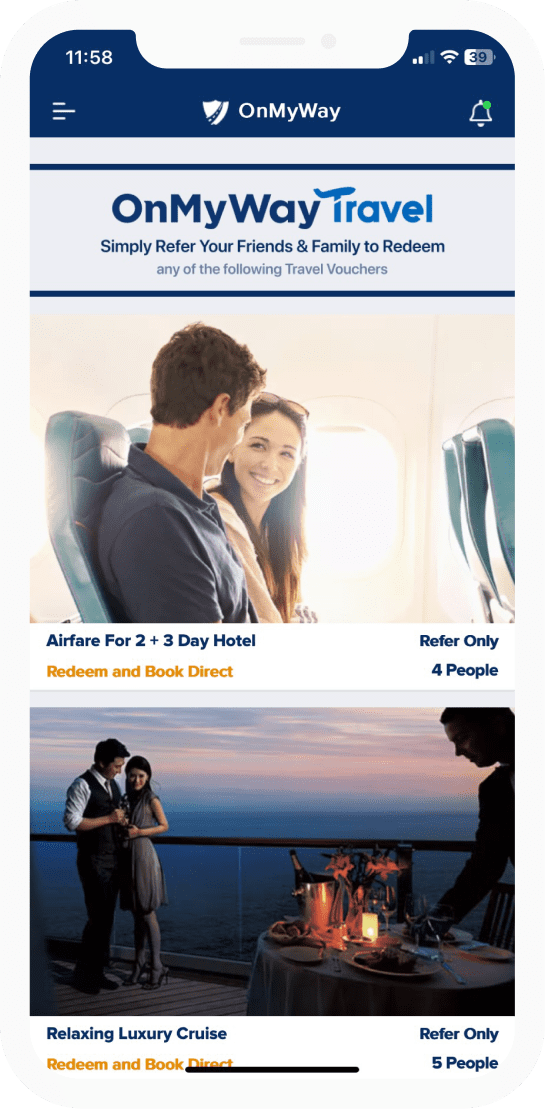
The money earned can then be used for Cash Cards, Gift Cards, Travel Deals and Much, Much More….
The company also makes it a point to let users know that OnMyWay does NOT sell users data and only tracks them for purposes of providing a better experience while using the app.
The OnMyWay app is free to download and is currently available on both the App Store for iPhones and Google Play for Android @ OnMyWay; Drive Safe, Get Paid.
Download App Now – https://r.onmyway.com
Sponsors and advertisers can contact the company directly through their website @ www.onmyway.com.
The company also makes it a point to let users know that OnMyWay does NOT sell users data and only tracks them for purposes of providing a better experience while using the app.