California, where earthquakes, droughts and wildfires have shaped life for generations, also faces the growing threat of another kind of calamity, one whose fury would be felt across the entire state.
This one will come from the sky.
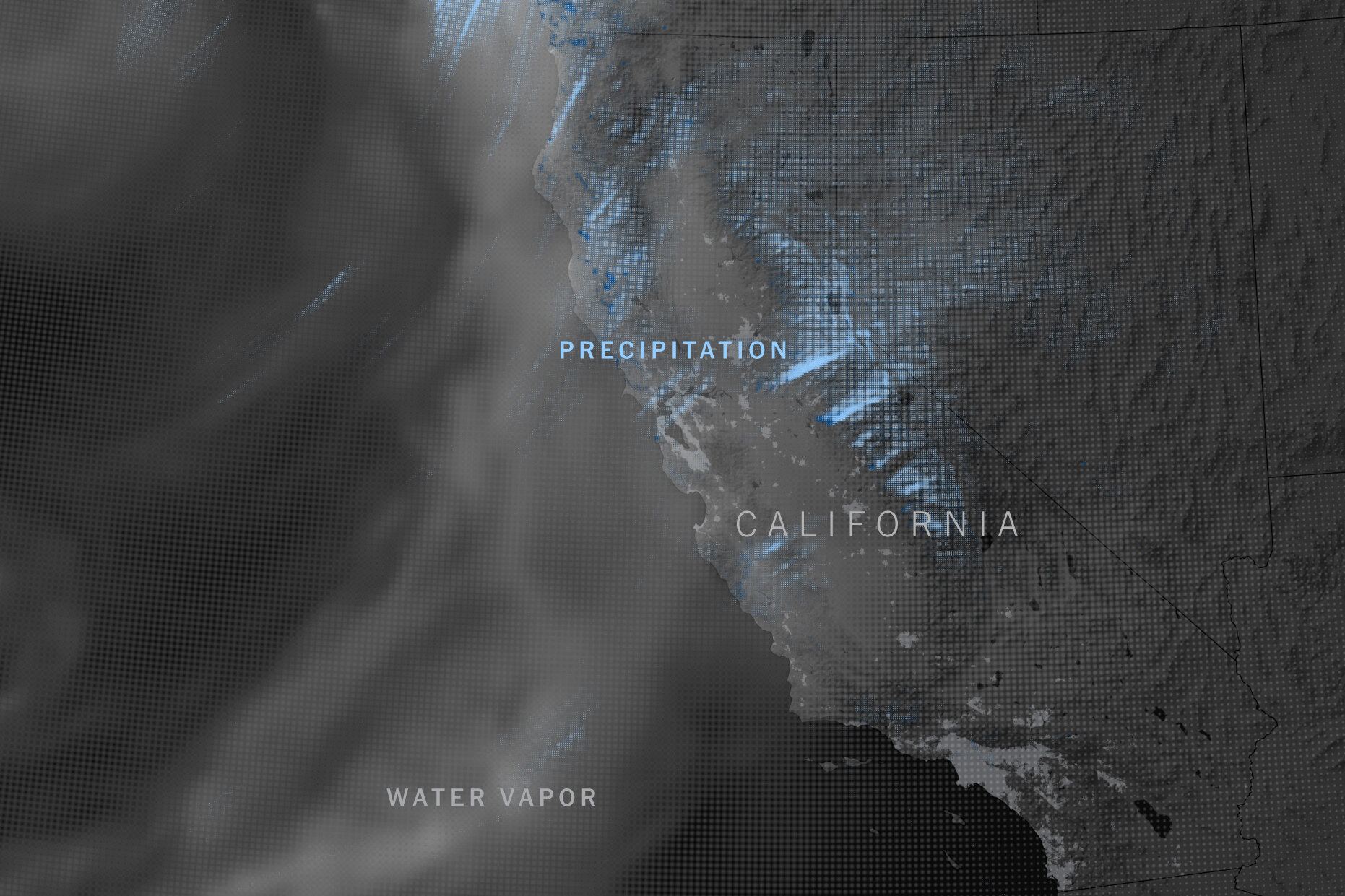
According to new research, it will very likely take shape one winter in the Pacific, near Hawaii. No one knows exactly when, but from the vast expanse of tropical air around the Equator, atmospheric currents will pluck out a long tendril of water vapor and funnel it toward the West Coast.
This vapor plume will be enormous, hundreds of miles wide and more than 1,200 miles long, and seething with ferocious winds. It will be carrying so much water that if you converted it all to liquid, its flow would be about 26 times what the Mississippi River discharges into the Gulf of Mexico at any given moment.
When this torpedo of moisture reaches California, it will crash into the mountains and be forced upward. This will cool its payload of vapor and kick off weeks and waves of rain and snow.
The coming superstorm — really, a rapid procession of what scientists call atmospheric rivers — will be the ultimate test of the dams, levees and bypasses California has built to impound nature’s might.
But in a state where scarcity of water has long been the central fact of existence, global warming is not only worsening droughts and wildfires. Because warmer air can hold more moisture, atmospheric rivers can carry bigger cargoes of precipitation. The infrastructure design standards, hazard maps and disaster response plans that protected California from flooding in the past might soon be out of date.
As humans burn fossil fuels and heat up the planet, we have already increased the chances each year that California will experience a monthlong, statewide megastorm of this severity to roughly 1 in 50, according to a new study published Friday. (The hypothetical storm visualized here is based on computer modeling from this study.)
In the coming decades, if global average temperatures climb by another 1.8 degrees Fahrenheit, or 1 degree Celsius — and current trends suggest they might — then the likelihood of such storms will go up further, to nearly 1 in 30.
At the same time, the risk of megastorms that are rarer but even stronger, with much fiercer downpours, will rise as well.
These are alarming possibilities. But geological evidence suggests the West has been struck by cataclysmic floods several times over the past millennium, and the new study provides the most advanced look yet at how this threat is evolving in the age of human-caused global warming.
The researchers specifically considered hypothetical storms that are extreme but realistic, and which would probably strain California’s flood preparations. According to their findings, powerful storms that once would not have been expected to occur in an average human lifetime are fast becoming ones with significant risks of happening during the span of a home mortgage.
“We got kind of lucky to avoid it in the 20th century,” said Daniel L. Swain, a climate scientist at the University of California, Los Angeles, who prepared the new study with Xingying Huang of the National Center for Atmospheric Research in Boulder, Colo. “I would be very surprised to avoid it occurring in the 21st.”
Unlike a giant earthquake, the other “big one” threatening California, an atmospheric river superstorm will not sneak up on the state. Forecasters can now spot incoming atmospheric rivers five days to a week in advance, though they don’t always know exactly where they’ll hit or how intense they’ll be.
Using Dr. Huang and Dr. Swain’s findings, California hopes to be ready even earlier. Aided by supercomputers, state officials plan to map out how all that precipitation will work its way through rivers and over land. They will hunt for gaps in evacuation plans and emergency services.
The last time government agencies studied a hypothetical California megaflood, more than a decade ago, they estimated it could cause $725 billion in property damage and economic disruption. That was three times the projected fallout from a severe San Andreas Fault earthquake, and five times the economic damage from Hurricane Katrina, which left much of New Orleans underwater for weeks in 2005.
Dr. Swain and Dr. Huang have handed California a new script for what could be one of its most challenging months in history. Now begin the dress rehearsals.
“Mother Nature has no obligation to wait for us,” said Michael Anderson, California’s state climatologist.
In fact, nature has not been wasting time testing California’s defenses. And when it comes to risks to the water system, carbon dioxide in the atmosphere is hardly the state’s only foe.
OVERVIEW
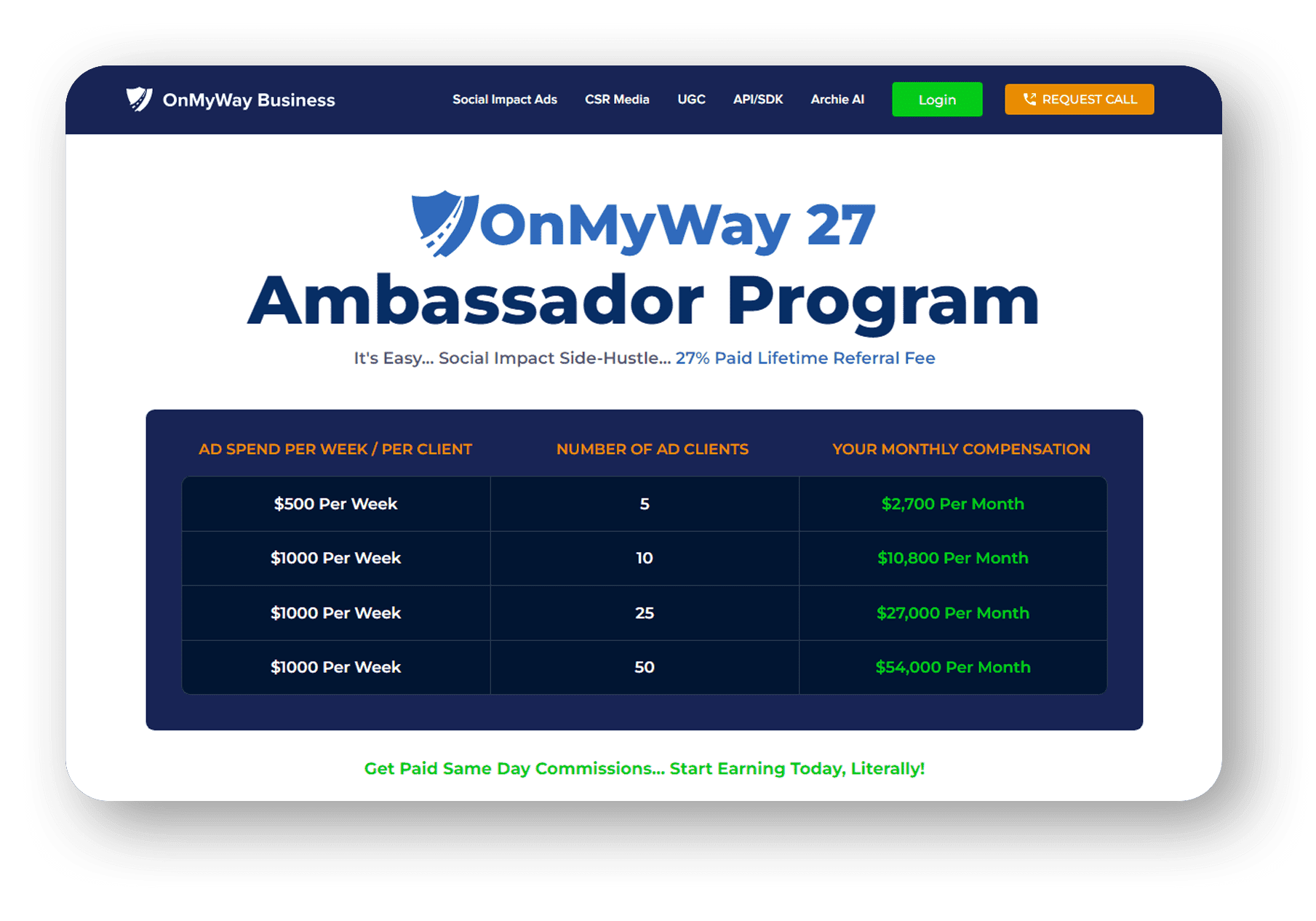
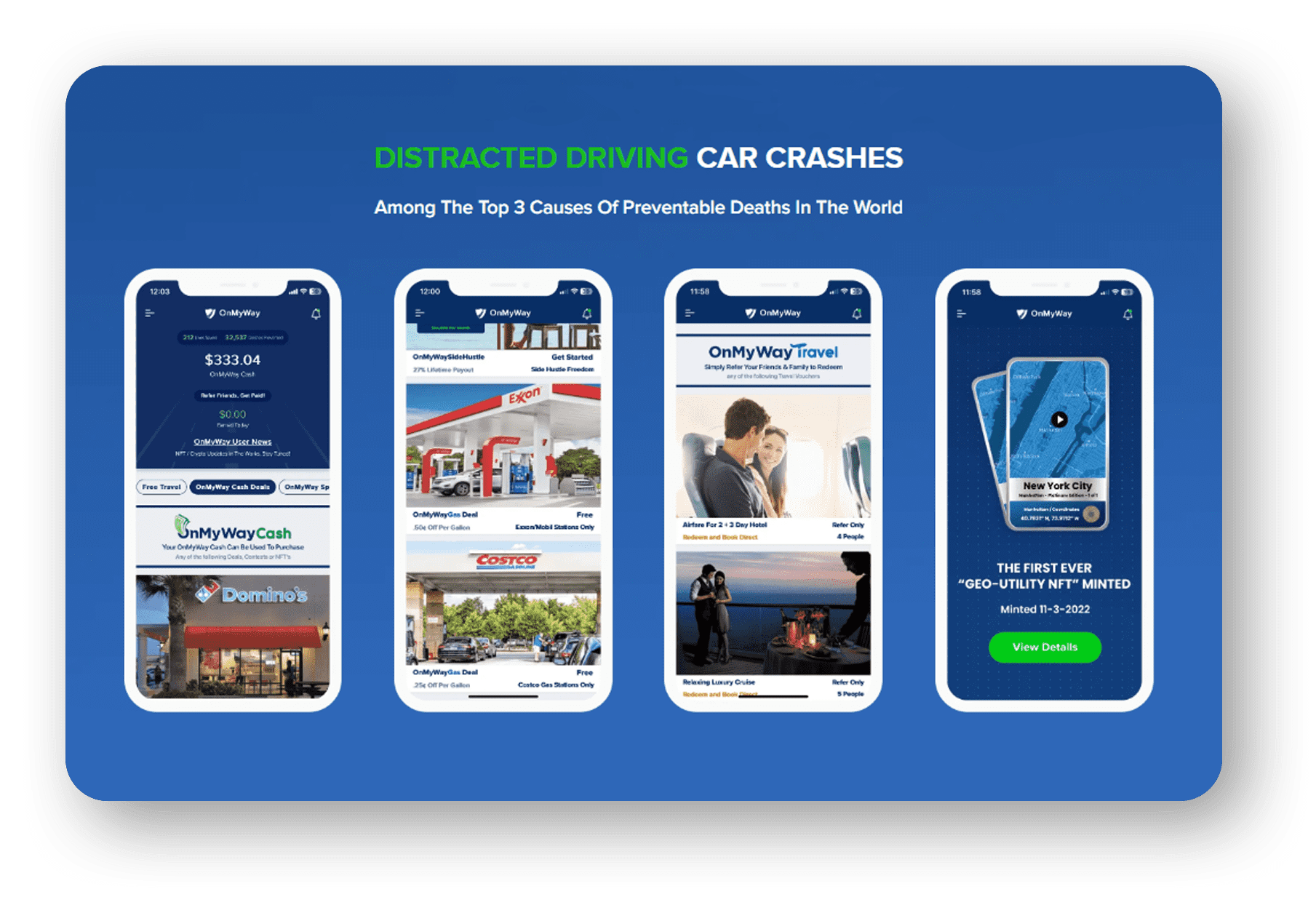
OnMyWay Is The #1 Distracted Driving Mobile App In The Nation!
OnMyWay, based in Charleston, SC, The Only Mobile App That Pays its Users Not to Text and Drive.
The #1 cause of death among young adults ages 16-27 is Car Accidents, with the majority related to Distracted Driving.
OnMyWay’s mission is to reverse this epidemic through positive rewards. Users get paid for every mile they do not text and drive and can refer their friends to get compensated for them as well.
The money earned can then be used for Cash Cards, Gift Cards, Travel Deals and Much, Much More….
The company also makes it a point to let users know that OnMyWay does NOT sell users data and only tracks them for purposes of providing a better experience while using the app.
The OnMyWay app is free to download and is currently available on both the App Store for iPhones and Google Play for Android @ OnMyWay; Drive Safe, Get Paid.
Download App Now – https://r.onmyway.com
Sponsors and advertisers can contact the company directly through their website @ www.onmyway.com.